Dr. Abhimanyu Rana
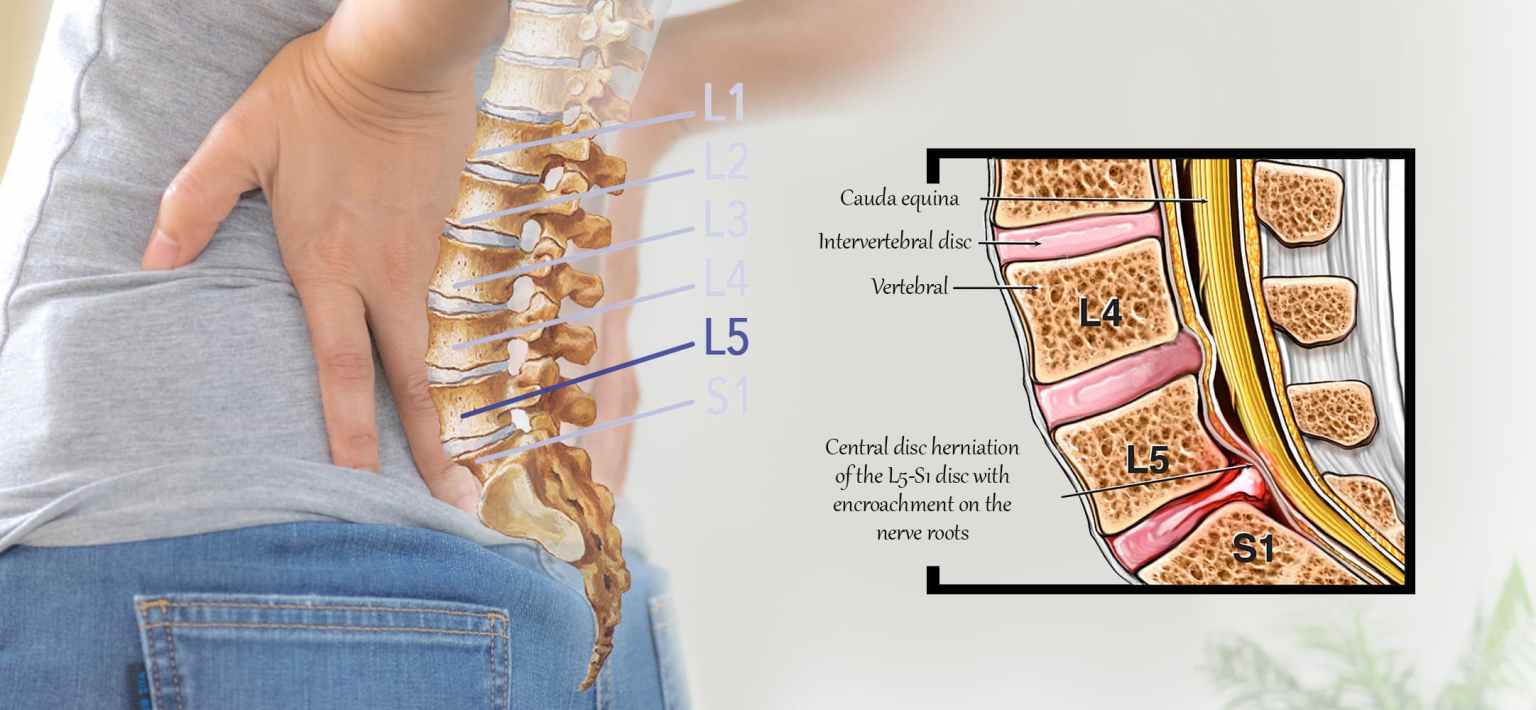
Back pain (including herniated discs and spinal stenosis)
Back pain is a common medical condition that can have various causes, and it can affect people of all ages. Two specific conditions you mentioned, herniated discs and spinal stenosis, are among the causes of back pain. Let's explore these conditions and their implications:
Herniated Disc (also known as a slipped disc or disc protrusion): A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner portion of a spinal disc (the gel-like nucleus pulposus) pushes through a weakened or damaged outer layer (the annulus fibrosus). This can lead to irritation or compression of nearby spinal nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, and weakness in the back, buttocks, legs, or feet, depending on the location of the herniation.
Treatment for herniated discs may include:
- Conservative measures: Rest, pain management with over-the-counter or prescription medications, physical therapy, and exercises to strengthen core muscles.
- Epidural steroid injections: These injections can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
- Surgical intervention: Surgery may be considered if conservative treatments are ineffective or if there is significant nerve compression causing severe symptoms.
Spinal Stenosis:Spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal or the spaces through which spinal nerves pass. This narrowing can result in pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness. Spinal stenosis can be either congenital (present from birth) or acquired (develops over time due to degenerative changes).
Treatment for spinal stenosis may involve:
- Conservative management: Similar to herniated discs, non-surgical approaches such as pain medications, physical therapy, and exercises are often recommended.
- Epidural injections: Steroid injections into the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: Surgical options may include decompressive laminectomy or minimally invasive procedures to create more space for the affected nerves.
It's important to note that back pain can have various other causes, including muscle strains, ligament sprains, degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis of the spine, and more. Proper diagnosis by a medical professional is crucial for determining the underlying cause of back pain and developing an appropriate treatment plan.

